SUPPORTING SKILLS
10 Steps for Managing Projects
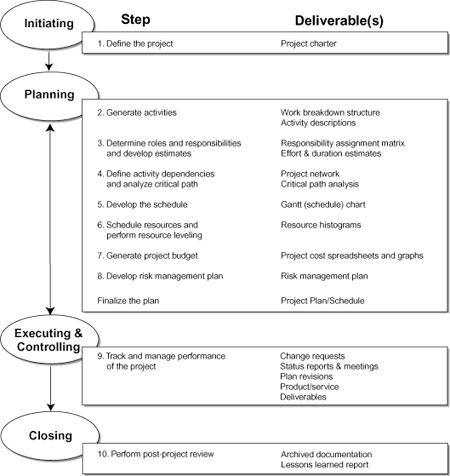
1. Define the Project
Defining the scope of the project is the first of ten steps for managing projects. Defining the scope is crucial to the success of the project, since it establishes a common understanding between the project customer and the project manager.
The process of defining the project involves seven steps:
- Determine the real need
- Define the end product/service
- Determine priorities for the project
- Develop a project mission statement
- Define your change control approach
- Establish the project infrastructure
- Prepare the project charter
Determine the Real Need
Determine the need that is driving the project. Ask why it is important to do the project now to substantiate the project’s importance.
Define the End Product/Service
Describe the end product/service in quantifiable terms. Include:
- Project deliverables
- Completion criteria - those things that tell us the project is finished
- Success criteria - those things that make the project successful
- Features and specifications
- Relevant quality standard
- Benefits
Determine Priorities for the Project
Discuss any project constraints with the customer to determine the driving factor for the project. The most important item to the customer is the most constrained, and cannot be adjusted.
Develop a Project Mission Statement
As discussed in Initiating, the project mission statement helps build enthusiasm and interest in the project and creates a common vision for its purpose and goals.
Define Your Change Control Approach
The change control process defines how change requestss to the project are received and assessed for impact, and then approved or disapproved.
Establish the Project Infrastructure
The project infrastructure serves to define the organizational structure for the project and establish the operational procedures.
Prepare the Project Charter
Discussed in detail in Initiating, the project charter provides the manager with the authority to use organizational resources on project activities.
2. Generate Activities
When you begin planning, look at how you are going to achieve the project objectives. This will determine what activities are going to take place.
Planning Horizon
Planning horizon refers to a technique that plans out as far as one can see and may be expressed as a number of days, a project phase, or the next major milestone. Developing estimates for work in the next planning horizon is more accurate than if developing estimates for the entire project.
The planning horizon is also known as the rolling wave method of planning.
WBS Process
Involve team members and subject matter experts (SMEs) when creating the WBS. The process involves six steps:
- Gather input from the project team by using questionnaires, interviews, group sessions, historical data, purchasing a methodology, and market analysis.
- Restate the project mission and objectives and confirm that they are correct.
- Decompose the project into level 1 categories, which are major elements of work or deliverables. Include both project management and product/service deliverables.
- Decompose each level 1 category into detailed activities and milestones that will comprise levels 2, 3, etc. of the WBS
- Identify an activity owner and deliverable for each activity at the lowest WBS level.
- Write an activity description for each activity.
3. Determine Roles & Responsibilities and Develop Estimates
Determine Roles & Responsibilities
Determining roles and responsibilities of all project participants requires careful selection of team members and identification of what each team member does on the project. According to the PMBOK® Guide, it involves identifying, documenting and assigning project roles and responsibilities, and reporting relationships.
To determine roles and responsibilities follow the five step process:
- Determine the roles and skills required to complete the deliverables based on the WBS.
- Select team members with the appropriate mix of skills.
- Discuss roles and responsibilities of team members relative to each activity.
- Gain commitment from the departments and individuals involved.
- Document roles and responsibilities
Develop Estimates
An estimate is a prediction of the time required to complete an activity. Three different types of estimates are required:
- Effort estimates reflect the amount of time an activity is expected to take to complete. This is normally represented in hours.
- Duration estimates reflect the work units needed to complete an activity. This is normally represented in days.
- Elapsed time reflects the number of calendar days over which an activity occurs.
The estimating process consists of five steps:
- Be sure each activity has been defined as clearly as possible.
- Collect relevant effort information from historical project data and use that to develop base estimates.
- Develop base estimates for the effort each person will contribute to an activity and the effort the entire team contributes to an activity, considering the level of variables.
- Determine whether the number of resources assigned to an activity influences it.
- Calculate a duration estimate for each activity.
4. Define Activity Dependencies and Analyze Critical Path
Define Activity Dependencies
Determine the logical order, or sequence, to perform activities. This is the last bit of information needed before producing the schedule.
Defining activity dependencies is a five step process:
- Make a Post-itTM note for each activity at the lowest WBS level.
- Identifying a starting activity. Place it at the left side of a flipchart page.
- Identify each activity’s immediate successor. Ask, "what activities must wait for this activity to finish before they can begin?" Place successor activities to the right of their predecessor.
- Determine the type of dependency relationship.
- Connect predecessor activities to successor activities with dependency arrows.
The result of this process is the project network diagram, a visual representation of activity dependencies.
As mentioned in step 4, multiple dependency types exist. Three of the dependency relationships are defined below:
- Finish-to-Start (FS) - The predecessor activity must be complete before its successor can start.
- Start-to-Start (SS) - The predecessor activity must start before the successor can start.
- Finish-to-Finish (FF) - The predecessor activity must be finished before the successor can finish.
Analyze Critical Path
The critical path is the longest series of activities in the project. It constitutes the shortest duration in which the project can be completed and denotes those activities without scheduling flexibility.
The critical path terminology includes:
- Early start is the earliest an activity can start.
- Early finish is the earliest an activity can finish, based on the activity’s early start and the activity’s duration.
- Late start is the latest an activity can start without delaying project completion based on the project completion date.
- Late finish is the latest an activity can finish without delaying project completion based on the end date.
- Float is the time an activity may be delayed from its early start, without delaying project completion.
- Duration is the business days needed to complete an activiy calculated from the start to finish.
The five steps in analyzing the critical path are:
- Take the project network and add the duration estimate to each activity node.
- Calculate early start and early finish dates by starting at the left (start) of the network and working forward to the right (end). This is often called a forward pass.
- Calculate the late start and late finish dates by starting at the right (end) of the network and working toward the left (start). This is often called a backward pass.
- Calculate the float for each activity.
- Identify and examine the critical path.
5. Develop the Schedule
A schedule shows the sequence of activities across time. This sequence is commonly shown on a Gantt chart, which is a time scale (calendar) bar chart.
You can develop the project schedule in four steps:
- Plot activities onto a Gantt chart based on the project network diagram.
- Indicate activity start and end points.
- Illustrate float and late finish to those activities not on the critical path.
- Add milestones to the schedule where appropriate.
6. Schedule Resources & Perform Resource Leveling
The resource scheduling and leveling process determines the scheduling of a resource or a pool of resources to simultaneous activities or projects.
It is the responsibility of the project manager to reschedule activities, re-prioritize work, or to negotiate for additional time, resources, or downsizing of scope, when you over-commit your resources.
To perform this step:
- Use individual assignments or calculated commitments posted on the schedule to schedule resources.
- Develop a resource histogram. (The histogram portrays the effort of the people working on the project in a time-scaled format.)
- Perform resource leveling, if needed.
Resource Leveling Options
Correct resource overloads or gaps can by using the following resource leveling techniques:
- Move activity into the float, finding a window resolving the overloading.
- Extend duration of the activity (within its available float) to decrease individual commitment.
- Allocate effort in a non-linear manner over the activity.
- Off-load the effort to someone else who has available time.
- Break dependencies, either starting sooner or ending later.
- Add people, overtime, technology, etc.
- Reduce scope.
- Push out the project end date.
7. Generate the Project Budget
The project budget allocates costs for labor, equipment, supplies, and other relevant expense categories over the duration of the project. The process involves four steps:
- Determine expense categories relevant to your project
- Build a basic periodic spreadsheet based on information from resource loading charts, the schedule, and activity descriptions.
- Use the periodic spreadsheet to formulate a cumulative spreadsheet.
- Build a line or bar graph based on periodic and/or cumulative project expenditures.
8. Develop a Risk Management Plan
Risk management identifies, assesses, and responds to potential risk events that might impact the project.
The development of the risk management plan involves six steps:
- Review the project plan with the team to identify risks that could adversely impact the project in the areas of scope, quality, schedule, costs, or team member’s availability.
- Determine the probable causes of the risk event.
- Evaluate the importance of each risk event by asking, "what is the probability that this risk will occur and what would be the impact if it does?"
- Determine the risk tolerance level with the project sponsor.
- For risks exceeding the tolerance level, the team develops a plan that includes:
- The overall priority of the risk
- An owner to monitor each risk event
- Mitigation strategies to prevent the risk from occurring or to reduce the impact if it occurs
- Contingency plan to implement if the risk occurs
- Add activities to the project schedule to include the activities to implement the mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
Finalizing the Plan
Final review of the plan ensures that implementation is attainable with the allocated resources, in the time allotted, and the cost parameter identified.
Documentation and approval of the final project plan ensures all project stakeholders understand the project and agree with the scope, time, and cost.
Finalizing the project plan is a four step process:
- Validate the plan.
- Obtain approvals.
- Set the baseline plan.
- Update the project repository.
Setting the baseline is a major project milestone. It indicates that planning is complete and is the formal commitment to time and cost. The baseline plan is:
- The official plan
- The basis for re-planning options
- Renegotiated when major changes to time, cost, or scope occur that warrant re-approvals
9. Track and Manage Performance of the Project
After initiating and planning are complete, work begins and the project manager’s job shifts to tracking and managing the performance of the project. This requires steps to ensure that actual performance matches the plan.
Tracking and managing the project occurs in a six step process:
- Collect actuals and forecasts
- Compare actual to plan
- Determine variance cause and analyze impact
- Take corrective action
- Make revisions to the project plan
- Report status and revisions
Collect Actuals and Forecasts
Categories you may measure or monitor include:
- Performance - deliverables completed, quality standards met
- Cost - work hours charged, overtime, purchase orders, invoices
- Schedule - start and completion dates and milestones met
- Staffing - work hours used, people participating
- Team morale and productivity
Compare Actual to the Plan
Compare plan to actual to reveal variances:
- Are you ahead or behind schedule?
- Are you under or over budget?
- Are you using the staff time you planned?
- Given actual staffing levels, are you getting the results you had expected?
Determine Variance cause and Analyze Impact
Variance is any difference between the plan and the actual or expected results. When variances occur look for the cause and assess their impact on the project.
Take Corrective Action
During the project, use corrective actions to ensure that actual performance conforms to the plan. The PMBOK® Guide defines corrective action as the "changes made to bring expected future performance of the project into line with the plan."
Make Revisions to the Project Plan
Based on corrective actions and progress to date, adjust the project plan to ensure that it remains a viable roadmap for all project participants.
Report Status and Revisions
As the team implements what you defined and planned for in the project, keep everyone informed, both in writing and in status meetings.
10. Perform Post-project Review
The final step in the project management processes is the closing process that wraps everything up. The post-project review is an meeting during which the project team evaluates the project as objectively as possible.
As discussed in closing, performing the post-project review involves three steps:
- Collect final actuals
- Conduct a post-project review meeting
- Document and archive project history
© 2006 Eviton LLC